Concepts¶
Architecture Overview¶
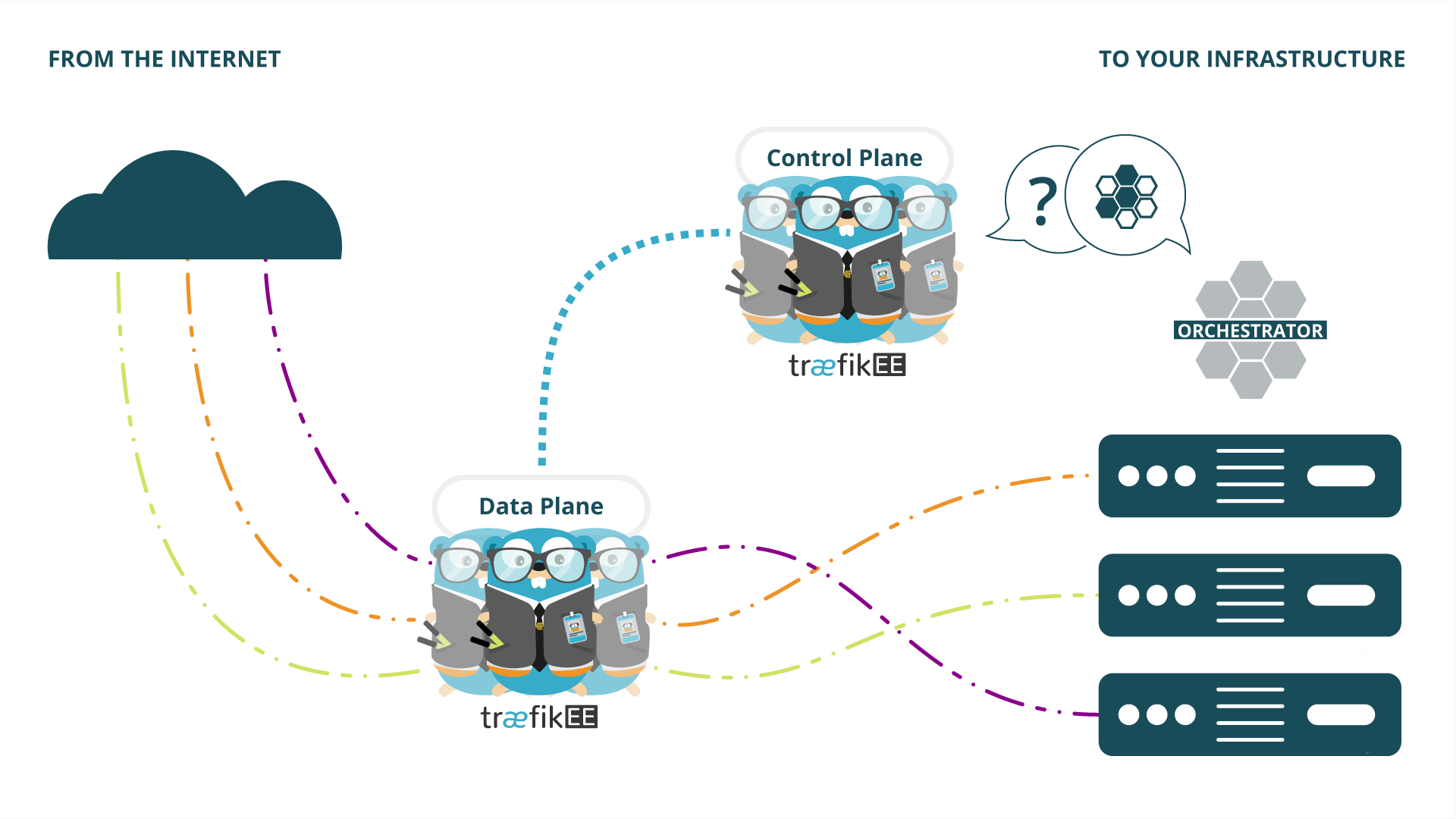
TraefikEE's architecture consists of nodes spread into two different planes: the control plane, and the data plane. The notions of control planes / data planes are not specific to Traefik and are well-known patterns.
As explained in the introduction:
- The data plane hosts horizontally scalable nodes that forward ingress traffic to your services.
- The control plane hosts distributed nodes that watch your platform and its services to configure the data plane.
This distributed architecture is the cornerstone of TraefikEE’s strengths: natively highly available, scalable, and secure.
Of course, every (non-deprecated) feature that is available for Traefik is also available for TraefikEE.
Nodes & Cluster¶
TraefikEE consists of a cluster of nodes communicating with one another. Each node is independent and belongs to either the control plane or the data plane.
Nodes in the Data Plane¶
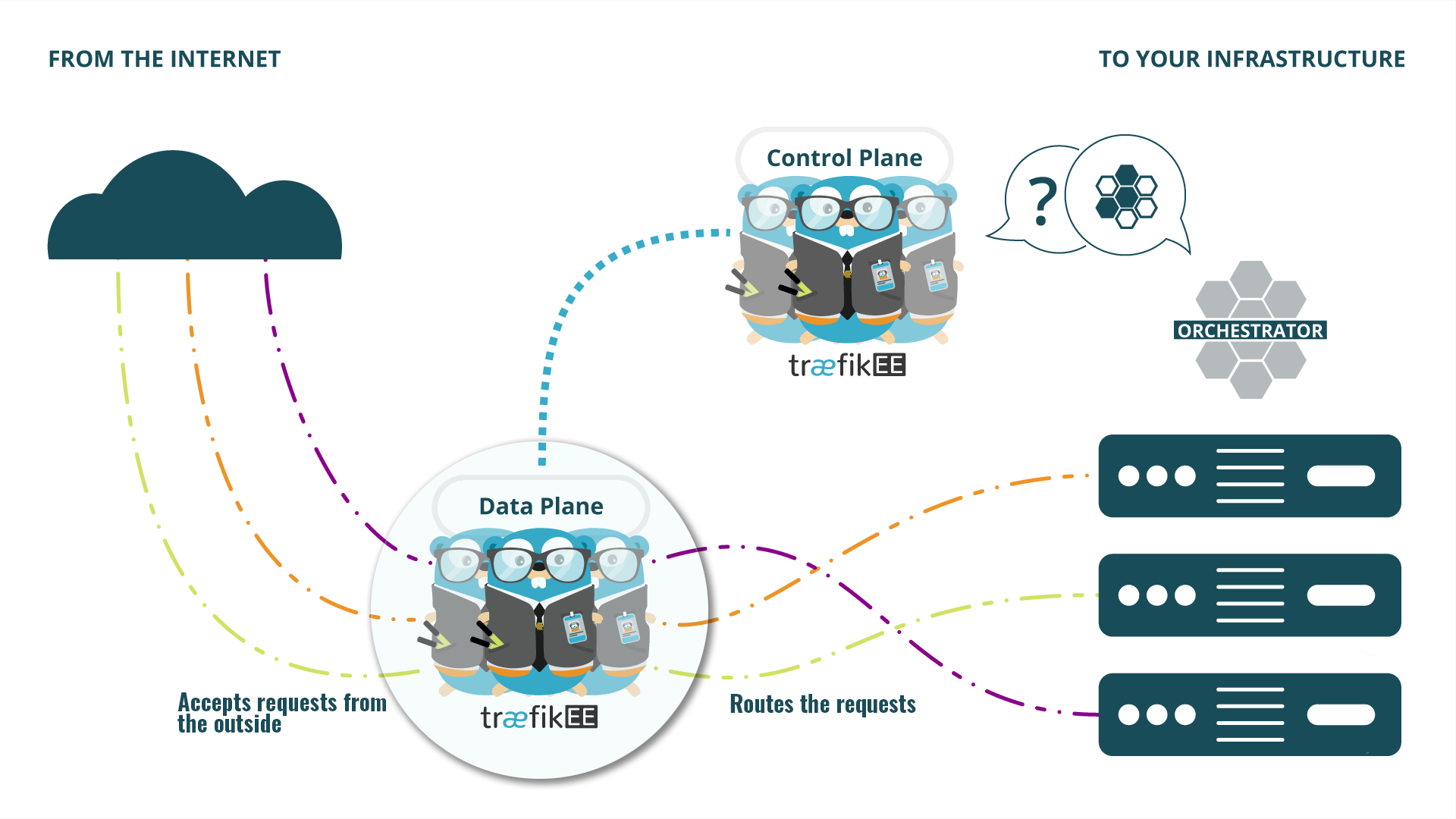
These nodes are the workers that route the incoming requests. You may view these nodes as regular Traefik instances that are automatically configured by other nodes from the control plane.
These nodes know nothing about your other infrastructure components and won't need to communicate with them.
Nodes in the Control Plane¶
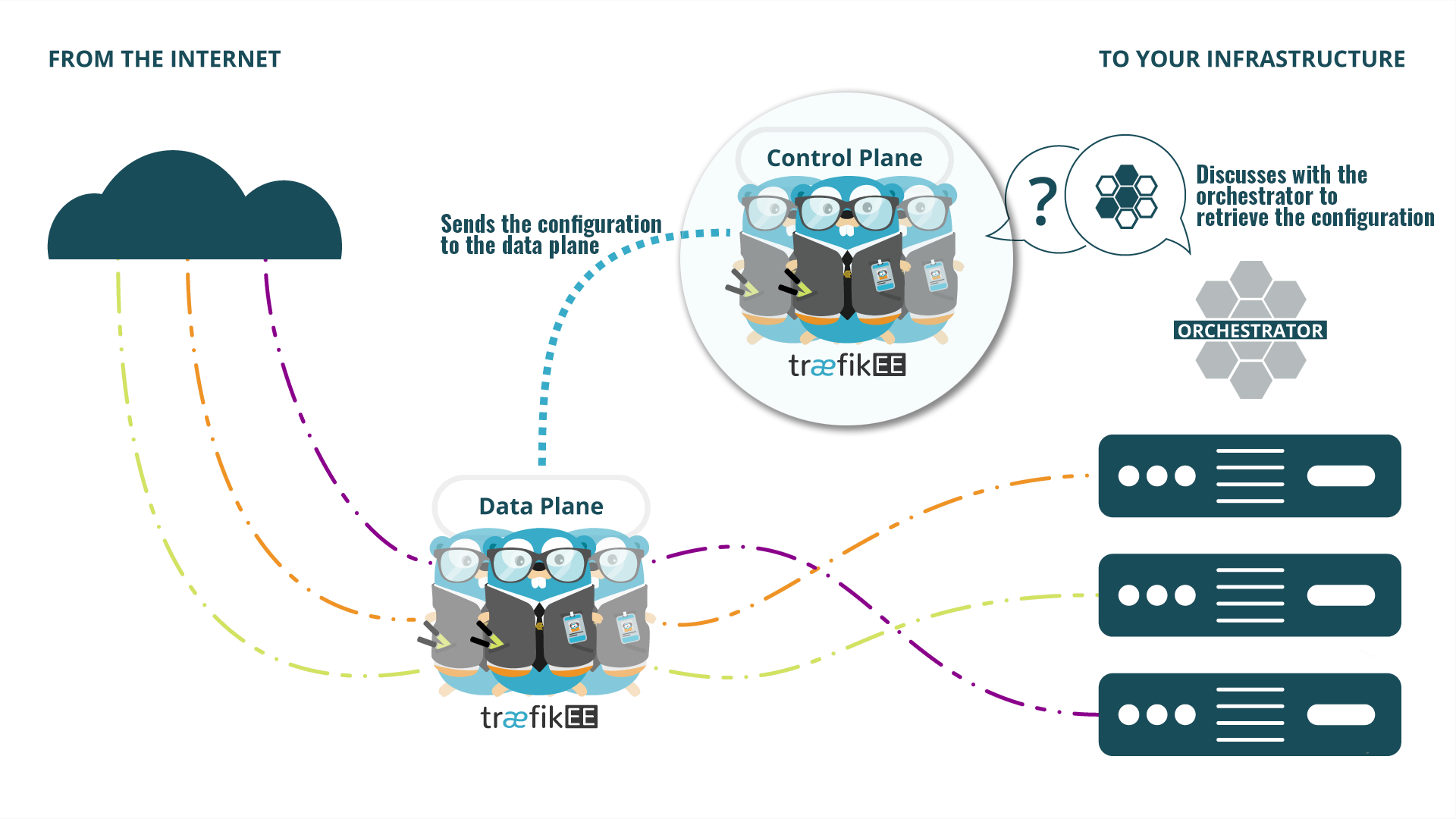
These nodes are responsible for querying your infrastructure components, creating the resulting configuration, and sending the routing instructions to the nodes in the data plane. These nodes will not handle incoming traffic.
Their main responsibilities are:
- Storing the data of the cluster, including events, certificates, and Traefik configuration.
- Sharing the data of the cluster as a distributed key-value store with all other nodes in the control plane.
- Propagating the latest configuration to the nodes in the data plane.
- Providing an API to configure the cluster and to query its state.
- Managing the dynamic configuration.
High Availability¶
TraefikEE's nodes work together to form a high-availability cluster.
TraefikEE uses the Raft protocol to manage its cluster.
Nodes in the cluster can have three different roles:
- Agent: node which accept requests on behalf of the leader
- Controller: agent responsible for querying your infrastructure components, the controllers form a quorum to assume the cluster HA
- Leader: controller responsible for updating/querying the state of the cluster
When a leader node becomes unavailable, if the quorum is not broken, the other controllers elect a new leader among the healthy controllers.
When a controller node becomes unavailable, if the number of controllers (including the leader) is not sufficient, the quorum is broken and the cluster is down.
When an agent node becomes unavailable, the cluster state doesn't change and it doesn't need to react.
If a new healthy node wants to join the cluster, it will participate as an agent or controller.
HA in the Data Plane¶
A node in the data plane is an agent.
Each node in the data plane can handle the routing for every configured request that arrives in your cluster. If a node becomes unavailable, the other nodes will take over and accept more incoming requests.
The data plane only needs one healthy agent to be functional.
HA in the Control Plane¶
Single Control Node Cluster¶
The node in the control plane is the leader.
It is responsible for the routing configuration and applying changes to the state of the cluster.
If the control node goes down, it can be automatically restarted. The cluster configuration will be restored automatically to the last state.
Multi Control Node Cluster¶
A node in the control plane is a controller which can be the leader too.
Nodes in the control plane are responsible for the routing configuration and applying changes to the state of the cluster.
A controller will send the configuration change requests to the leader who will then update the cluster state.
Common Questions¶
How Many Nodes Do You Need in the Control Plane?¶
The cluster is healthy as long as the nodes in the control plane can reach a quorum to elect a new leader in case of failure.
The quorum is (N-1)/2 where N is the initial number of nodes in the control plane.
If the number of healthy nodes goes below this number, the cluster must recover before it resumes normal operations.
What Happens if the Control Plane is Unhealthy?¶
The data plane will continue to route the requests based on the latest known configuration.
Scalability¶
Both the data plane nodes and the control plane nodes can be scaled horizontally by deploying more nodes.
Each node in the data plane can handle every configured request to your cluster. Load balancing the incoming requests between TraefikEE's data plane nodes is achieved by your infrastructure components (e.g., using Services in Kubernetes).
Note about Auto Scaling
Depending on your infrastructure components, you may benefit from auto-scaling tools that will help you automatically scale up/down your nodes as needed. For instance, for Kubernetes, here is a guide to set up a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
Scaling the control plane
When a TraefikEE cluster is bootstrapped with one control node (the default value) it is impossible in TraefikEE to scale the control plane. However, it is possible to perform a backup and restore operation and change the number of control nodes on the restored cluster during installation.
When a TraefikEE cluster is bootstrapped with many control nodes once a cluster is installed, it is possible to scale the control nodes thanks to the orchestrator commands. Also, please make sure to always use an odd number of nodes.
Security¶
TraefikEE makes sure your data is safe. Nodes discuss using GRPC and encrypt their communication using mutual TLS.
On top of that, not only having two separate planes for handling different responsibilities improves the resilience of your cluster, but it also improves its security: nodes in the control plane are not exposed to the outside, making an attack against your infrastructure more difficult.
What's Next?
Now that you have a basic overview of TraefikEE's concepts, maybe you'd like to familiarize yourself even more with the vocabulary and cast a glance at the glossary?
Or you might want to learn more with other resources such as blog posts or videos, found in the "Learn" -> "Resources" page?