Traefik Hub AI Gateway
The AI Gateway adds a thin, dedicated control layer on top of Traefik Hub’s API Gateway. It focuses on chat‑completion traffic and other LLM calls and exposes a set of specialised middlewares you can attach to any route.
Why Traefik Hub AI Gateway?
| Challenge | What the AI Gateway brings |
|---|---|
| Multiple provider SDKs, inconsistent request formats | Route every request through one gateway using a single, OpenAI‑compatible JSON schema. |
| Model & parameter sprawl | Apply governance policies in one place (lock or allow overrides for model, temperature, topP, etc.). |
| High inference costs & duplicate calls | Use the Semantic Cache middleware to reuse previous responses for semantically similar requests, cutting token spend and latency. |
| Safety, compliance, data‑loss prevention | Run Content Guard rules on requests and responses before they reach the model. |
| Visibility into cost drivers | Export GenAI‑specific metrics (semconv) and traces to your existing backend. |
| Run several local models behind one endpoint | Use the Model(`<pattern>`) matcher to route by model field in the JSON body. |
Two Personas, Two Modes
| Persona | Goal | Typical topology |
|---|---|---|
| API Publisher | Strictly control which external LLMs and models consumers may call. | Client → Hub AI Gateway → Provider Cloud |
| Model‑as‑a‑Service Provider | Expose all local models with all tunable options. | Client → Hub API Gateway → Hub AI Gateway → Cluster of local models |
The same AI Gateway binary serves both use‑cases. You decide the behaviour by attaching (or omitting) middlewares and by toggling model‑override settings.
How It Works
-
Enable the AI Gateway feature. Set the dedicated flag in your Helm values (see Enabling the AI Gateway below).
-
Attach AI middlewares to a route. A route becomes an “AI endpoint” as soon as you add at least one AI middleware—typically chat-completion.
-
(Optional) Match on model before routing. Use the
Model(`<pattern>`)matcher to direct traffic to different services inside the cluster.
Supported AI Providers
Traefik Hub works with any provider that exposes an OpenAI‑compatible chat‑completion endpoint. Verified providers include:
- OpenAI
- Azure OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Cohere (Compatibility API)
- DeepSeek
- Gemini
- Mistral
- Ollama
- Qwen
- Amazon Bedrock
- Local models served via KServe, vLLM, or similar
Provider Compatibility Information
Here is a list of providers and their compatibility information:
| Provider | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Cohere | Compatibility API |
| Anthropic | OpenAI SDK |
| Gemini | OpenAI |
| Ollama | OpenAI Compatibility |
| Mistral | API |
| Amazon Bedrock | AWS |
Enabling the AI Gateway
To enable the AI Gateway, you can add the following to your Helm values or install configuration:
- Helm
- Install Configuration
helm upgrade traefik traefik/traefik -n traefik --wait \
--reset-then-reuse-values \
--set hub.aigateway.enabled=true \
--set hub.aigateway.maxRequestBodySize=10485760 # optional, default to 1MiB
--hub.aigateway=true
--hub.aigateway.maxRequestBodySize=8388608 # Optional
hub.aigateway.enabled=true: turns on all AI features.
hub.aigateway.maxRequestBodySize: hard limit for the size of request bodies inspected by the gateway (protects against OOM/DoS attacks). Accepts a plain integer representing bytes, for example10485760for 10 MiB. The default value is1048576(1 MiB).
AI Middlewares
Traefik Hub AI Gateway ships four purpose‑built middlewares you can attach individually or in combination to any route:
| Middleware | What it does |
|---|---|
| Chat Completion | Turns any route into a chat-completion endpoint, adds GenAI metrics, and enforces (or lets clients override) model/parameter settings. |
| Semantic Cache | Stores and replays responses when a new request is semantically similar, cutting token spend and latency. |
| Content Guard | Inspects prompts and completions for policy violations before they reach or leave the model. |
| LLM Guard | Provides flexible content security using external guard services or LLMs with custom templates and powerful expression-based blocking conditions. |
Each middleware is configured in its own Kubernetes Middleware resource and can be chained like any other Traefik Hub middleware.
The four middlewares can be chained; order matters for streaming and compression (see individual docs).
Request‑Body Limits & Model Matcher Costs
The flag hub.aigateway.maxRequestBodySize protects Traefik Hub from oversized
bodies and from requests that use chunked upload (Content‑Length: -1).
- If the body exceeds the limit, the gateway returns 413 Payload Too Large.
- If the request is chunked, the gateway returns 400 Bad Request.
Model(`<pattern>`) needs to read the body during the routing phase.
For best performance:
- Put more‑selective matchers (
Host(),PathPrefix(), etc.) beforeModel()so non‑AI traffic is routed without parsing bodies. - Give routes that contain
Model()a lower priority than normal API routes.
When using Model() matchers with hub.aigateway.maxRequestBodySize, the behavior differs:
- The Model matcher reads the entire request body to evaluate the pattern
- If the body exceeds the size limit, the matcher treats it as "not matching" rather than returning 413
- The request falls through to the next matching route without raising an error
- This allows oversized requests to be handled by non-AI routes while protecting AI endpoints
Frequently Asked Questions
I’m seeing a log error that says chat completion middleware requires an AI gateway configuration. What does this mean?
This message means that the AI Gateway feature is not enabled for the Traefik Hub instance handling your request.
- Helm users: add
hub.aigateway=truein yourvalues.yamlor helm install command. - Non-Kubernetes users: start Traefik Hub with the
--hub.aigateway=trueflag in the install configuration. Once the flag is active, restart Traefik Hub and the error will disappear.
How do I rotate an upstream provider's API key without downtime?
Update the token or apiKey reference in your middleware resource.
Because this key is only used between Traefik Hub and the upstream LLM provider, no client-side changes are required. Existing applications
keep calling the same Hub endpoint while the gateway transparently switches to the new credentials.
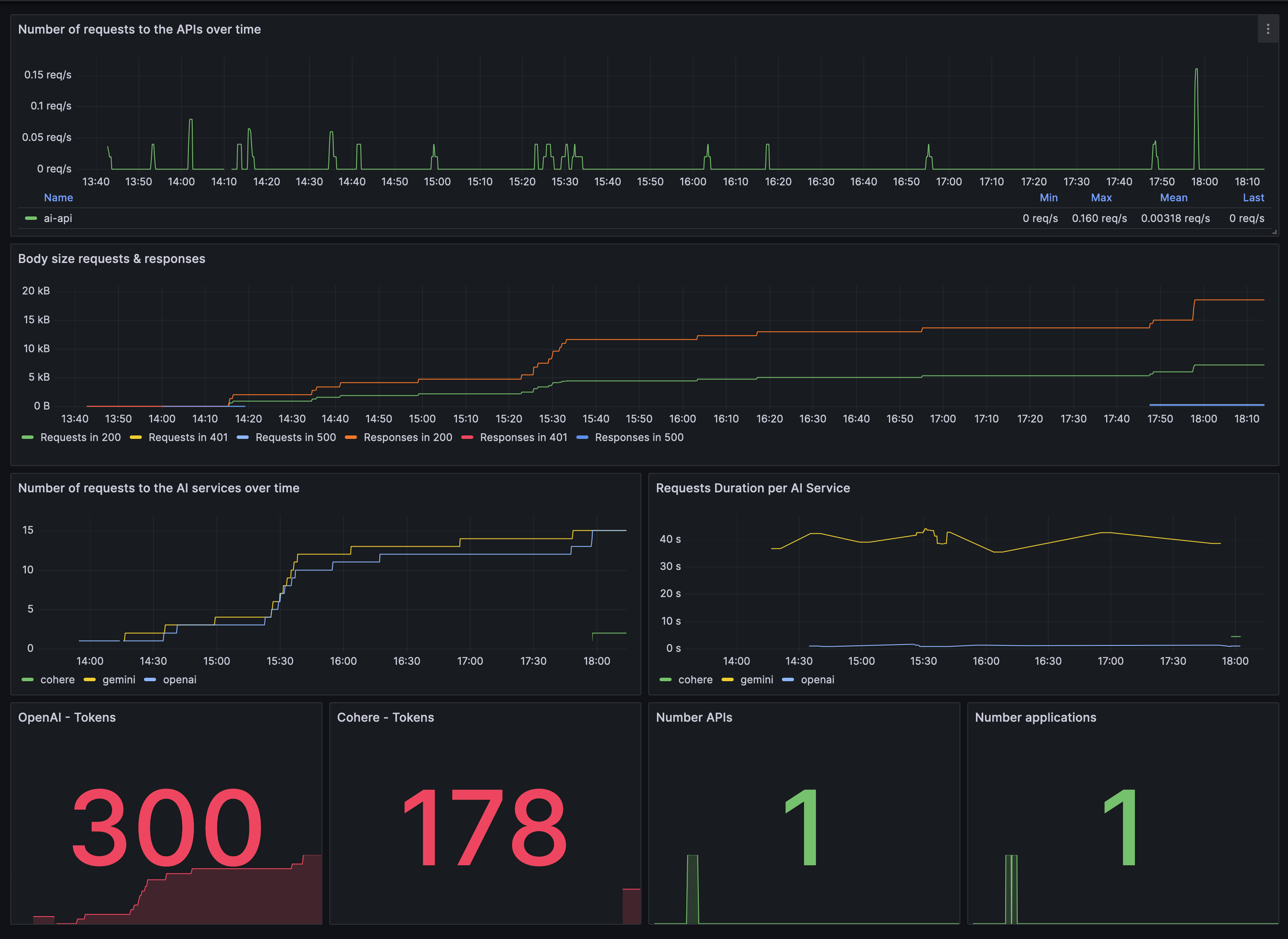
Can I monitor AI service performance?
Yes, Traefik AI Gateway integrates with OpenTelemetry to provide detailed metrics on token usage and operation durations. You can visualize these metrics using monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana.
Can I still use the Content Guard Middleware on normal APIs?
Yes, as long as the AI Gateway flag is enabled. Attach the generic content-guard middleware to any route—even non‑AI traffic.
Does model‑based routing hurt performance?
Only the routes that include a Model() matcher trigger body parsing. Use narrow route prefixes and set priorities, so non‑AI traffic bypasses the matcher.
