APIAuth
Configure API authentication with the APIAuth Custom Resource Definition (CRD).
Introduction
The APIAuth resource provides a declarative way to configure authentication for your APIs in Traefik Hub API Management. This resource works in both online and offline environments, allowing you to manage API authentication
settings through Kubernetes manifests.
APIAuth enables per-namespace authentication overrides, allowing you to run different authentication methods on the same gateway by placing APIs in different namespaces. Previously, this required separate Hub workspaces
and separate gateways. Now your workspace settings act as a "global default" that you can override on a per-namespace basis with CRDs.
When defined, the CRD configuration takes precedence over workspace-level dashboard settings.
APIAuth works seamlessly in both online and offline modes.
In online environments, it integrates fully with self-service & managed applications, allowing users to create API keys through the Developer Portal
while respecting the authentication method defined in the APIAuth resource.
In offline environments where connectivity to the Traefik Hub Online Dashboard is restricted, APIAuth allows you to maintain full control
over API authentication while operating in air-gapped environments.
Example Use Case: You can now have APIs in the payments namespace using JWT authentication, APIs in the public namespace using API Key authentication, and APIs in the internal namespace using your workspace default
authentication method - all on the same gateway!
The APIAuth resource supports three authentication methods:
- API Key Authentication: Key-based authentication with API keys
- JWT Authentication: Token-based authentication using JSON Web Tokens
- LDAP Authentication: Basic Auth authentication validated against LDAP servers
Namespace Scope and Default Behavior
The APIAuth CRD is namespace-scoped, meaning it applies to all APIs within the same namespace. This design follows the principle of least privilege while providing convenient management for APIs grouped by namespace.
isDefault Behavior
APIAuth resources are only recognized when isDefault is set to true. Resources with isDefault: false or without this property will be ignored by the system. When isDefault: true is configured,
the authentication method applies to all APIs within the same namespace. If multiple APIAuth resources exist in a namespace with isDefault: true, the system will use the first one when sorted alphabetically by name.
Configuration Example
Basic Structure
- API Key
- JWT
- LDAP
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: auth-config
namespace: apps
spec:
isDefault: true
apiKey: {} # API Key authentication
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: auth-config
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt: {} # JWT authentication
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: auth-config
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
ldap:
url: ldaps://ldap.example.com:636
baseDN: dc=example,dc=org
bindDN: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=org
bindPasswordSecretName: ldap-bind-secret
searchFilter: (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid=%s))
Configuration Options
| Field | Description | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
isDefault | Specifies if this APIAuth should be the default authentication method for the namespace. | Yes | - |
| Authentication Method | Exactly one of apiKey, jwt, or ldap must be specified. | Yes | - |
API Key Authentication
API Key authentication provides an authentication method using pre-shared keys. In online environments, users can create self-service applications and generate API keys through the Developer Portal. In offline or declarative scenarios, API keys are managed by ManagedApplication resources.
Configuration Example
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: apikey-auth
namespace: production
spec:
isDefault: true
apiKey: {}
The apiKey configuration requires no additional properties. Authentication is handled through API keys created either via self-service applications in the Developer Portal or
through ManagedApplication resources.
JWT Authentication
JWT authentication validates JSON Web Tokens using various verification methods.
Configuration Example
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: jwt-auth
namespace: production
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: azp
jwksUrl: https://auth.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
Configuration Options
| Field | Description | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
jwt.appIdClaim | Name of the JWT claim containing the application identifier | Yes | - |
jwt.trustedIssuers | List of trusted JWT issuers with their JWKS endpoints. See Multiple Trusted Issuers for details. Recommended for multi-tenant scenarios. | No | - |
jwt.jwksUrl | URL to fetch JWKS for JWT verification. For multi-tenant scenarios with multiple identity providers, consider using trustedIssuers instead. | No | - |
jwt.jwksFile | JWKS file content for JWT verification. | No | - |
jwt.publicKey | PEM-encoded public key for JWT verification. | No | - |
jwt.signingSecretName | Name of Kubernetes Secret containing signing secret. The secret must be of type Opaque and contain a key named value. | No | - |
jwt.stripAuthorizationHeader | Whether to strip Authorization header before forwarding. | No | false |
jwt.tokenQueryKey | Query parameter name for JWT token. If not set, only the Authorization header is used. | No | - |
jwt.forwardHeaders | Additional headers to forward with the request. | No | - |
jwt.tokenNameClaim | JWT claim for token name (used in metrics). | No | - |
Exactly one of trustedIssuers, jwksUrl, jwksFile, publicKey, or signingSecretName must be specified.
Multiple Trusted Issuers
The trustedIssuers field enables a single APIAuth resource to validate JWTs from multiple identity providers, making it ideal for multi-tenant scenarios where different tenants use different
identity providers (for example, Tenant A uses Auth0, Tenant B uses Okta, Tenant C uses Azure AD).
Each trusted issuer configuration includes:
jwksUrl(required): The HTTPS URL to fetch the JWKS fromissuer(optional): The expected value of theissclaim in the JWT
Issuer Validation:
- When
issueris specified, tokens must have this exact issuer value to be validated against this JWKS - When
issueris omitted, this JWKS acts as a fallback for tokens from any issuer - Only one fallback entry (without
issuer) is allowed perAPIAuthresource - Issuer values must be unique across all entries
Configuration Options:
| Field | Description | Required | Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|
trustedIssuers[].jwksUrl | HTTPS URL to fetch the JWKS from | Yes | Must be a valid HTTPS URL |
trustedIssuers[].issuer | Expected value of the iss claim | No | Must be unique if specified |
Example Configurations:
- Multiple Specific Issuers
- Mix of Specific and Fallback
- Single Fallback
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: multi-tenant-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: sub
trustedIssuers:
- jwksUrl: "https://tenant-a.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://tenant-a.auth0.com/"
- jwksUrl: "https://tenant-b.okta.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://tenant-b.okta.com/"
- jwksUrl: "https://tenant-c.azuread.net/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://tenant-c.azuread.net/"
This configuration validates tokens from three different identity providers, each with explicit issuer validation.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: mixed-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: client_id
trustedIssuers:
- jwksUrl: "https://primary.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://primary.example.com/"
- jwksUrl: "https://fallback.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
This configuration validates tokens from a specific issuer and includes a fallback JWKS for tokens from other issuers.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: fallback-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: sub
trustedIssuers:
- jwksUrl: "https://auth.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
This configuration validates tokens from any issuer using a single JWKS endpoint.
- Maximum of 100 trusted issuers per
APIAuthresource - All
jwksUrlvalues must use HTTPS - Issuer values must match exactly, including trailing slashes and URL encoding
- Only one trusted issuer may omit the
issuerfield (acting as a fallback) trustedIssuersis mutually exclusive withjwksUrl,jwksFile,publicKey, andsigningSecretName
JWT Verification Methods
Choose the appropriate JWT verification method based on your authentication provider:
- Trusted Issuers
- JWKS URL
- JWKS File
- Public Key
- Signing Secret
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: trusted-issuers-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: sub
trustedIssuers:
- jwksUrl: "https://issuer1.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://issuer1.example.com/"
- jwksUrl: "https://issuer2.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json"
issuer: "https://issuer2.example.com/"
Use this method for multi-tenant scenarios or when you need to support multiple identity providers. See Multiple Trusted Issuers for detailed information.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: jwks-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: azp
jwksUrl: https://auth.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
Use this method when your JWT issuer provides a JWKS endpoint. Most OAuth2 providers support this.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: jwks-file-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: client_id
jwksFile: |
{
"keys": [
{
"kty": "RSA",
"kid": "example-key-id",
"use": "sig",
"n": "...",
"e": "AQAB"
}
]
}
Use this method for static JWKS configuration when you have the key set available.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: pubkey-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: sub
publicKey: |
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA...
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
Use this method when you have a static public key for verification.
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: secret-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: aud
signingSecretName: jwt-signing-secret
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: jwt-signing-secret
namespace: default
type: Opaque
data:
value: <base64-encoded-secret>
Use this method for symmetric key verification with secrets stored in Kubernetes.
OAuth2 Provider Integration
Single Provider
Below is an example of how to configure APIAuth for Auth0:
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: auth0-integration
namespace: api-services
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: azp
jwksUrl: https://your-domain.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json
forwardHeaders:
X-User-ID: sub
X-User-Email: email
Multiple Providers (Multi-Tenant)
For multi-tenant scenarios where different customers use different OAuth2 providers, use trustedIssuers:
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: multi-tenant-oauth2
namespace: api-services
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: azp
trustedIssuers:
# Tenant A using Auth0
- jwksUrl: https://tenant-a.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json
issuer: https://tenant-a.auth0.com/
# Tenant B using Okta
- jwksUrl: https://tenant-b.okta.com/oauth2/default/.well-known/jwks.json
issuer: https://tenant-b.okta.com/oauth2/default
# Tenant C using Azure AD
- jwksUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant-c-id/discovery/v2.0/keys
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant-c-id/v2.0
forwardHeaders:
X-User-ID: sub
X-User-Email: email
LDAP Authentication
LDAP authentication validates API requests using Basic Authentication credentials against an LDAP server. This method is particularly useful for organizations that already have an LDAP infrastructure and want to leverage it for API authentication.
How LDAP Authentication Works
When using LDAP authentication with APIAuth:
- API consumers send requests with Basic Auth credentials (
Authorization: Basic <base64(username:password)>) - The username from Basic Auth must match an
appIdin a ManagedApplication resource - Traefik Hub validates the credentials against the configured LDAP server
- If both LDAP authentication succeeds AND the application has valid access via ManagedSubscription, the request proceeds
LDAP authentication for APIs requires:
- Valid LDAP credentials (username/password validated against LDAP)
- A ManagedApplication with
appIdmatching the LDAP username - A ManagedSubscription granting that application access to the API
Configuration Example
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: ldap-auth
namespace: production
spec:
isDefault: true
ldap:
url: ldaps://ldap.example.com:636
baseDN: dc=example,dc=org
bindDN: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=org
bindPasswordSecretName: ldap-bind-secret
searchFilter: (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid=%s))
Configuration Options
| Field | Description | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
ldap.url | LDAP server URL, including protocol (ldap:// or ldaps://) and port (for example, ldaps://ldap.example.com:636) | Yes | - |
ldap.baseDN | Base domain name for bind and search queries (for example, dc=example,dc=org) | Yes | - |
ldap.bindDN | Domain name to bind for authentication when running in search mode. If empty, anonymous bind is used (not recommended for production) | No | - |
ldap.bindPasswordSecretName | Name of Kubernetes Secret containing the bind password (must be the value of a key named password) | No | - |
ldap.attribute | LDAP object attribute used to form bind DN. Bind DN format: <attribute>=<username>,<baseDN> | No | cn |
ldap.searchFilter | LDAP search filter query. Use %s as placeholder for username (for example, (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid=%s))) | No | - |
ldap.startTLS | Enable StartTLS when initializing connection with LDAP server | No | false |
ldap.insecureSkipVerify | Skip TLS certificate verification (not recommended for production) | No | false |
ldap.certificateAuthority | PEM-encoded certificate for TLS connection with custom Certificate Authority | No | - |
LDAP Bind Password Secret
Create a Kubernetes Secret containing the LDAP bind password:
- kubectl
- YAML
kubectl create secret generic ldap-bind-secret \
--from-literal=password=your-bind-password \
-n production
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: ldap-bind-secret
namespace: apps
type: Opaque
data:
password: <base64-encoded-bind-password>
The LDAP bind password secret must contain a key named password.
LDAP Provider Examples
- OpenLDAP
- Active Directory
- Oracle Internet Directory
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: openldap-api-auth
namespace: apps
spec:
isDefault: true
ldap:
url: ldaps://openldap.example.com:636
baseDN: dc=example,dc=org
bindDN: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=org
bindPasswordSecretName: ldap-bind-secret
searchFilter: (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid=%s))
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: ad-api-auth
namespace: apps
spec:
isDefault: true
ldap:
url: ldaps://ad.example.com:636
baseDN: dc=example,dc=com
bindDN: cn=Service Account,ou=Service Accounts,dc=example,dc=com
bindPasswordSecretName: ad-bind-secret
searchFilter: (&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName=%s))
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: oid-api-auth
namespace: apps
spec:
isDefault: true
ldap:
url: ldaps://oid.example.com:636
baseDN: dc=example,dc=com
bindDN: cn=orcladmin
bindPasswordSecretName: oid-bind-secret
searchFilter: (&(objectClass=person)(uid=%s))
LDAP with ManagedApplications
When using LDAP authentication, create ManagedApplication resources where the appId matches the LDAP username:
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedApplication
metadata:
name: john-doe-app
namespace: apps
spec:
appId: john.doe # Must match LDAP username
owner: john.doe # LDAP username
notes: "Application for John Doe"
# No apiKeys section needed - authentication is done via LDAP
For production systems, it's recommended to use separate LDAP accounts for the owner (human user) and appId (machine/application user):
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedApplication
metadata:
name: website-app
namespace: apps
spec:
appId: svc.website # Machine user - authenticates API requests
owner: john.doe # Human user - manages app in portal
notes: "Website backend service"
This separation provides operational resilience:
- API requests use the machine user credentials (
svc.website) - Portal access is managed by the human user (
john.doe) - If
john.doeleaves the company, thesvc.websiteservice account continues to function without disruption - The
ownercan be reassigned to a different human user, allowing the new owner to manage the application in the portal
This pattern is especially important for long-running services and prevents service disruption due to employee turnover.
When the user john.doe makes a request with Basic Auth using their LDAP password, Traefik Hub will:
- Validate the credentials against LDAP
- Match the username
john.doeto theappIdin the ManagedApplication - Check if a ManagedSubscription grants access to the API
- Allow or deny the request based on all validations
Configuration via Dashboard UI
You can also configure API authentication through the Traefik Hub Dashboard UI in addition to using CRDs.
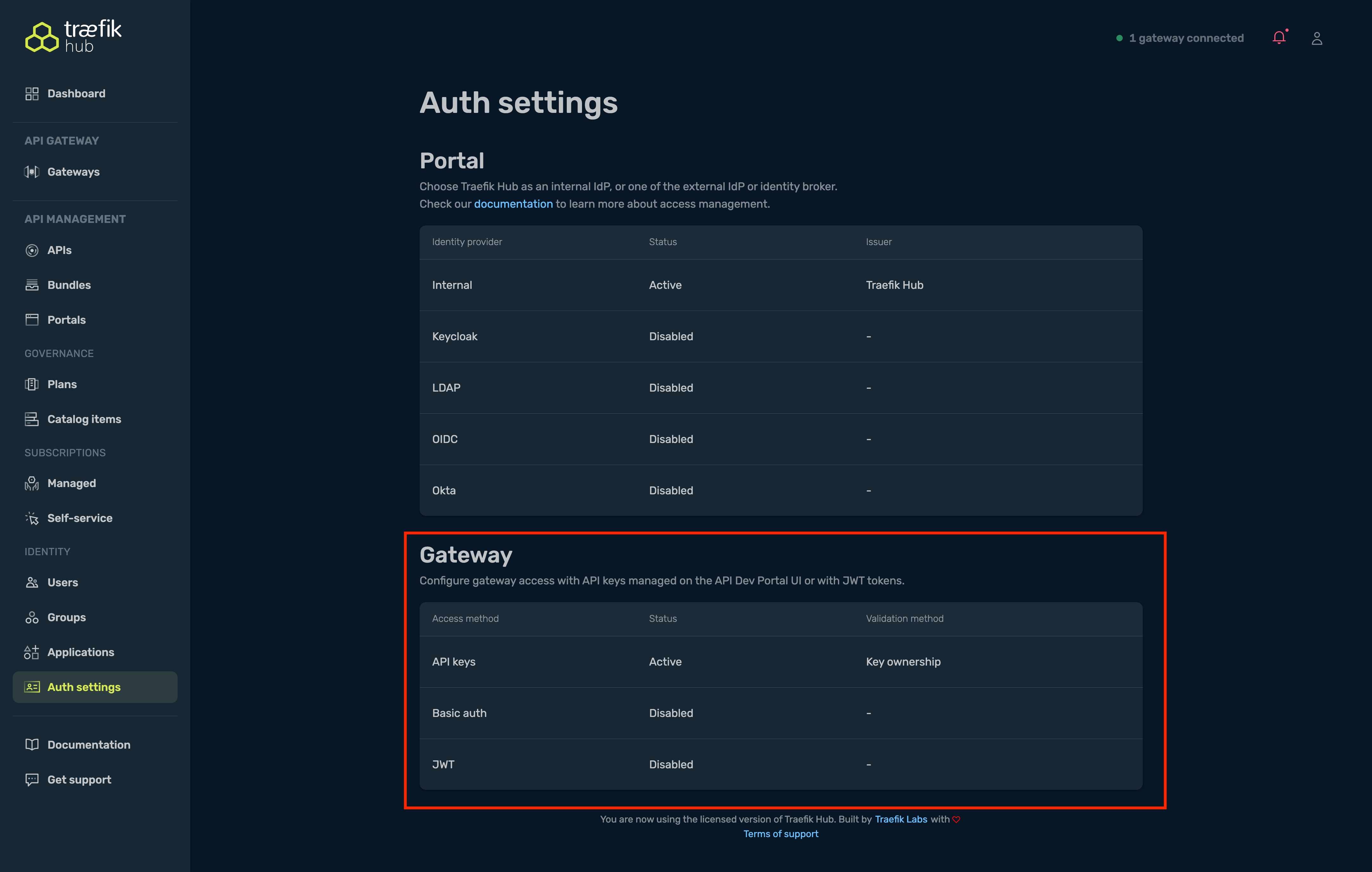
- UI Configuration: Convenient for quick setup and testing, configuration stored in Traefik Hub platform. The UI setting is global for the entire workspace and applies to all APIs across all clusters and namespaces.
- CRD Configuration: Infrastructure as Code approach, version controlled, essential for offline environments. APIAuth CRDs are namespace-scoped, allowing different authentication methods per cluster or per namespace within the same workspace.
- Precedence: CRD configuration takes precedence over UI configuration when both are defined
This namespace-scoped approach enables advanced scenarios like having JWT authentication in the payments namespace,
API Key authentication in the public namespace, and LDAP authentication in the internal namespace - all within the same workspace on the same gateway.
Migration from Dashboard Configuration
When migrating from online dashboard authentication to APIAuth CRDs:
- Identify Current Settings: Note your authentication configuration from the online dashboard
- Create APIAuth Resource: Convert dashboard settings to APIAuth CRD format
- Deploy and Validate: Use the Traefik Hub static analyzer to ensure correct configuration
- Test Authentication: Verify that APIs continue to authenticate properly
Migration Example
Dashboard JWT configuration with Auth0:
- JWKS URL:
https://auth.company.com/.well-known/jwks.json - App ID Claim:
azp - Forward email as header:
X-User-Email
Equivalent APIAuth CRD with Auth0:
apiVersion: hub.traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: APIAuth
metadata:
name: migrated-auth
namespace: default
spec:
isDefault: true
jwt:
appIdClaim: cid
jwksUrl: https://your-domain.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json
forwardHeaders:
X-User-Email: email
Troubleshooting
- APIs not authenticating: Ensure
APIAuthresource exists in the same namespace as your APIs withisDefault: true. - Multiple authentication methods: Verify only one authentication method (apiKey, jwt, or ldap) is specified in the
APIAuthresource. - JWT verification failing: Check that your JWKS URL is accessible and contains the correct public keys.
- Missing application identifier: Ensure the
appIdClaimmatches the claim name in your JWT tokens. - Trusted issuers validation errors:
- Verify all
jwksUrlvalues use HTTPS (HTTP is not allowed) - Check that issuer values are unique across all trusted issuers
- Ensure only one trusted issuer omits the
issuerfield (fallback) - Confirm the
issclaim in your JWT exactly matches the configured issuer value, including trailing slashes
- Verify all
- Trusted issuers mutual exclusivity: If you receive an error about multiple JWT verification methods, ensure you're using only
trustedIssuersand not combining it withjwksUrl,jwksFile,publicKey, orsigningSecretName. - LDAP authentication failing: Verify LDAP server connectivity, bind credentials, and that the username matches a ManagedApplication
appId.
Related Content
- Learn more about the APIPortalAuth in its dedicated section.
- Learn more about ManagedApplication in its dedicated section.
- Learn more about the API object in its dedicated section.
- Learn more about Offline Mode in its dedicated section.
