JSON Web Tokens
JWT, or JSON Web Token, is a compact and self-contained method for transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. JWTs are used for API authorization.
Introduction
Every consumer in Traefik Hub is connected to an API Portal user. The user access settings determine which APIs and API Portal the consumer can access.
In Traefik Hub, every user needs to be part of a user group. It is not possible to assign an individual user to an API, however you can assign a user to a group as the only member.
When a user is a member of multiple groups, the user will inherit the permission level of the group with the most access.
Please refer to the user management documentation for more information.
If you switch from the default configuration (Key authentication) to JSON Web Tokens, all API keys generated in the API Portal are turned off.
JWT Validation
JWT claims are statements in key-value pair format about an entity (typically, the user) and additional data that are digitally signed to ensure their integrity. For validation, Traefik Hub expects to find the following claims in the payload.
Claims Mapping
Claims mapping lets you specify which fields in the JWT payload should be used for access control and metrics. The most common claims are:
| Field | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Claim that identifies the application (for example, cid, azp, or client_id). | cid | Yes* |
| Token | Claim used as the application name in metrics. | token | No |
Client ID is required for application-level access control. Token is optional and only needed for labeling traffic in metrics.
For more information about JWT claims, see the official JWT documentation.
Enable JWT in Traefik Hub
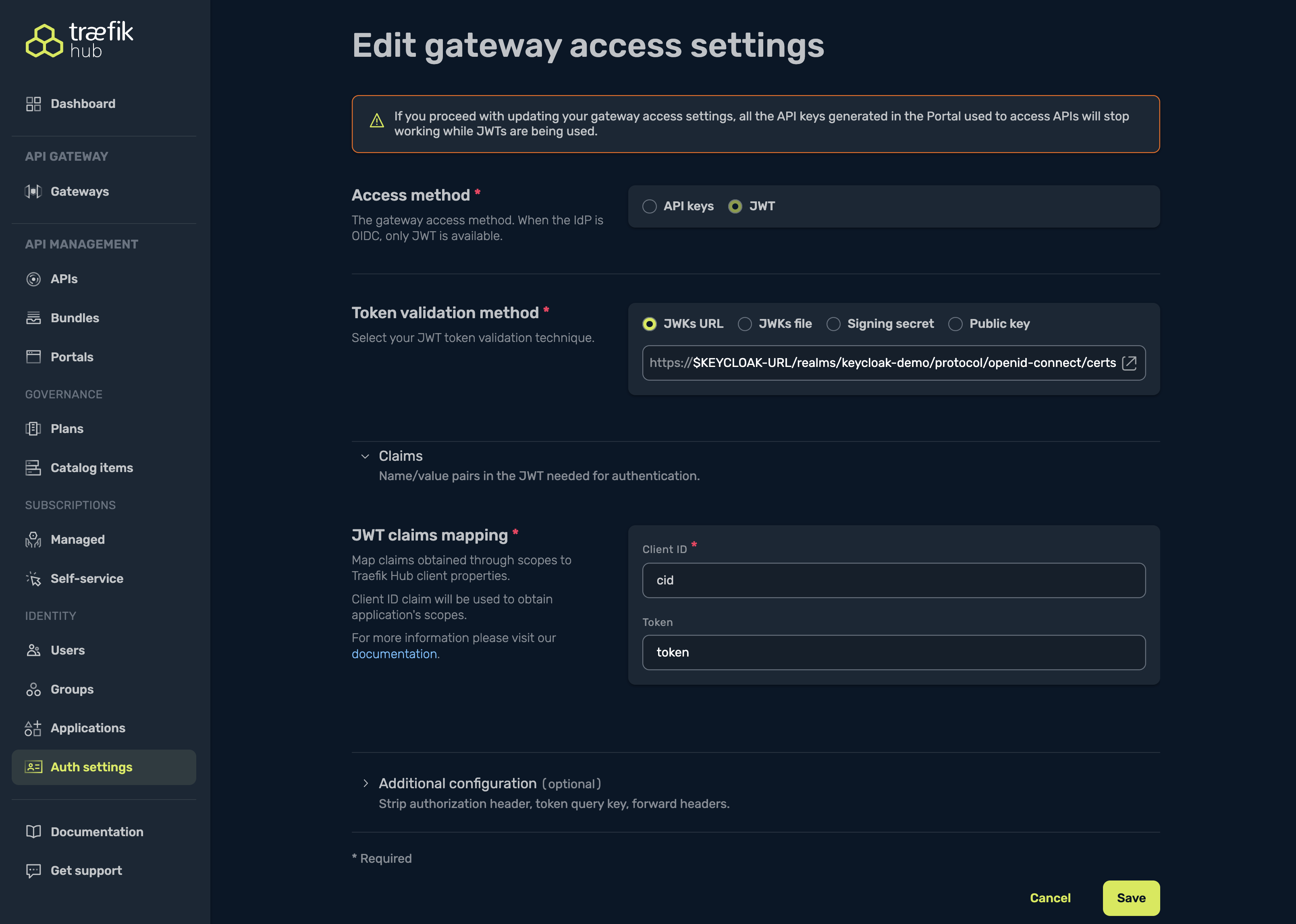
Open Auth settings in the dashboard. In the Gateway section, select JWT as the access method. The UI will present a form with several configuration options:
Access Method
Choose between API keys and JWT. When JWT is selected, all API keys generated in the Portal will stop working. This is enforced immediately after saving.
Token Validation Method
Select how Traefik Hub should validate incoming JWTs:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
signingSecret | The signingSecret option can be set to the secret used for signing the JWT certificates. |
publicKey | The publicKey option can be used as an alternative to a signing secret to verify incoming requests. In that case, users should sign their token using a private key, and the public key can be used to verify the signature. |
jwksFile | The jwksFile option can be used to define a set of JWK to be used to verify the signature of JWTs. |
jwksUrl | The jwksUrl option can be used as an alternative to a signing secret to verify incoming requests. It is the URL of the host serving a JWK set. This option can either be set to a full URL, for example https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certs. |
Example (JWKs URL):
https://$KEYCLOAK-URL/realms/keycloak-demo/protocol/openid-connect/certs
Claims Mapping
Map JWT claims to Traefik Hub fields:
| Field | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Claim that identifies the application (for example, cid, azp, or client_id). | cid | Yes* |
| Token | Claim used as the application name in metrics. | token | No |
Example:
- Client ID:
cid - Token:
token
Advanced JWT Configuration
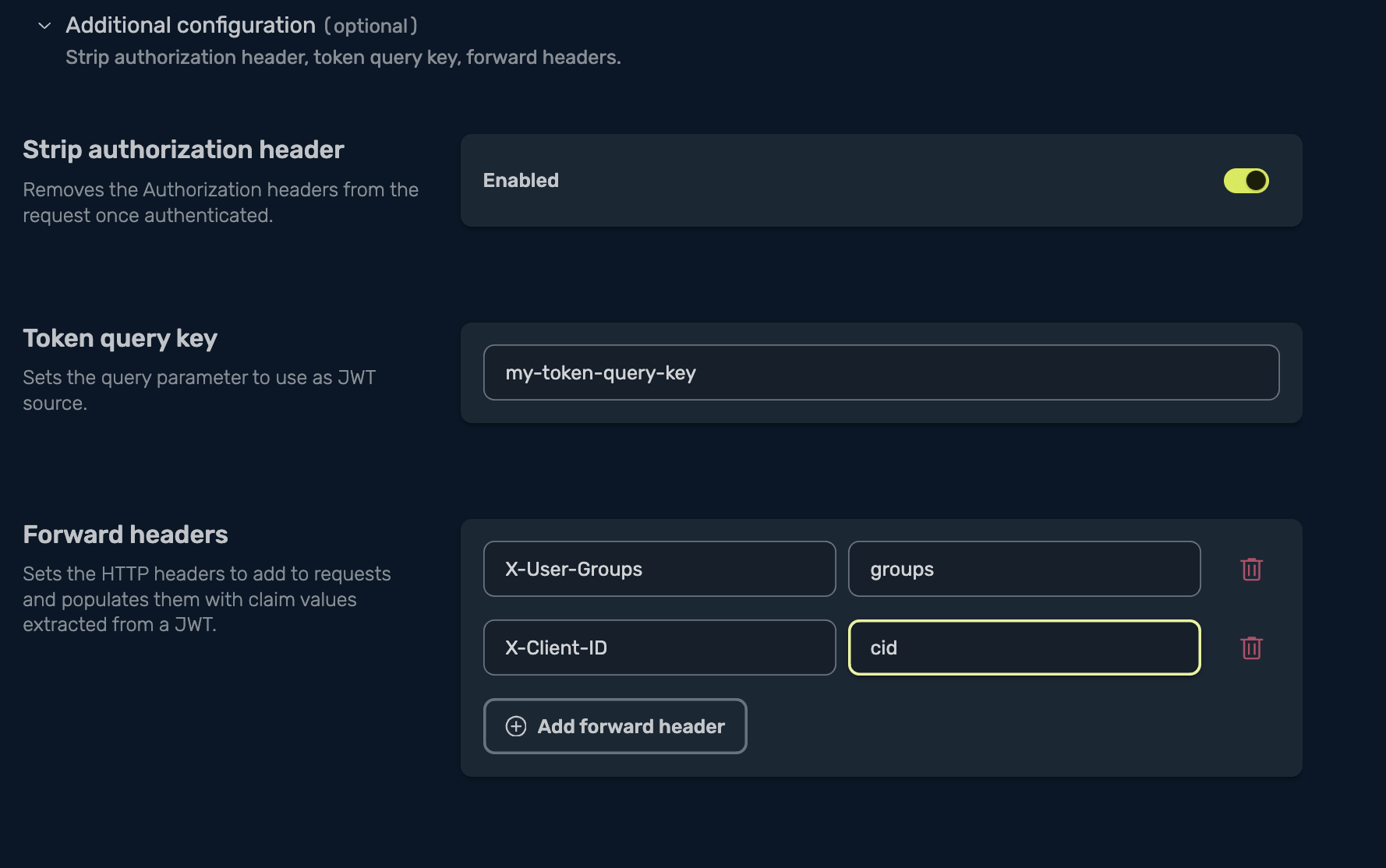
Expand the Additional configuration section to access advanced options:
Strip Authorization Header
Removes the Authorization header from the request after the JWT is validated. This is useful if you do not want upstream services to see the original token. Toggle this option as needed.
Token Query Key
Allows clients to pass the JWT as a query parameter instead of an Authorization header. Enter the name of the query parameter to use (for example, my-token-query-key). This is only recommended for clients that cannot set headers.
Forward Headers
Copies specific claims from the JWT into HTTP headers on the upstream request. For each header, specify the header name and the claim to extract.
Example:
- Header:
X-User-Groups, Claim:groups - Header:
X-Client-ID, Claim:cid
Once you have completed the configuration, select Save. All API clients must now send Authorization: Bearer <jwt> with a token signed by your IdP.
Any existing Portal-generated API keys will stop working immediately.
JWT Authentication Example
The following example uses curl to send test requests to an API using JWT as the authentication method.
curl -i --url 'https://api.example.com/tickets/tickets' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer abCdeFciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbkBleGFtcGxlLmNvbSIsIm5hbWUiOiJteS10b2tlbiIsImdyb3VwcyI6WyJhZG1pbiJdfQ.INzvgtArvSYdz3CDTresRdcmwPKocgEsFv_aH123456'
Which will show:
HTTP/2 200
access-control-allow-credentials: true
access-control-allow-origin: *
content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
date: Wed, 31 Jan 2024 15:42:15 GMT
x-ratelimit-limit: 2000
x-ratelimit-period: 65
x-ratelimit-remaining: 1999
x-ratelimit-reset: 1
content-length: 326
{
"tickets": [
{ "id": 1, "flightCode": "TL123", "fare": 500, "class": "first", "available": 5, "total": 20 },
{ "id": 2, "flightCode": "TL234", "fare": 200, "class": "economy", "available": 2, "total": 5 },
{ "id": 3, "flightCode": "TL345", "fare": 300, "class": "business", "available": 3, "total": 10 }
]
}
Related Content
- Learn how to use JWT validation with Keycloak.
- Learn how to validate JWT with Okta.
